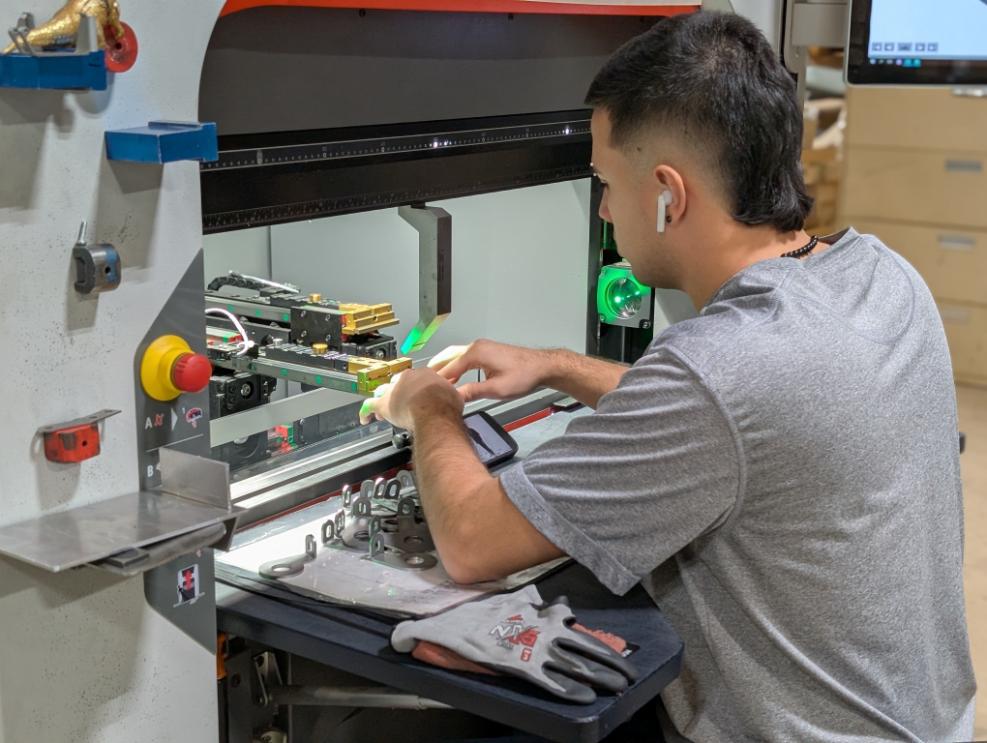
The Sheet Metal Stamping Process: How It Works and Where It’s Used
Sheet metal stamping is one of the most essential manufacturing processes used today. If you’ve ever wondered how intricate metal components are created at high volumes with incredible precision, the answer often lies in metal stamping. From small electronic parts to structural automotive components, stamped metal parts appear in almost every industry.
From understanding what sheet metal stamping is to how it works and the materials involved, we’ll show why this process is both efficient and cost-effective.
What Is Sheet Metal Stamping?
Sheet metal stamping is a manufacturing process that transforms flat sheet metal into precise, three-dimensional parts. Using specialized tools called dies, a stamping press applies significant force to cut, bend, or form the metal into a desired shape.
In simple terms:
Flat sheet in → precise metal part out.
Stamping can produce simple shapes or extremely complex geometries. That’s why it’s used for everything from rapid prototyping to mass-produced components in industries like automotive, aerospace, industrial equipment, and consumer appliances.
How Sheet Metal Stamping Works
Although the stamping process can include many individual steps, most operations rely on three key components:
- The sheet metal
- The stamping die
- The press machine
Here’s how the process typically works.
1. Forming
In forming, the flat metal sheet is reshaped by applying force with a forming die. This creates a new geometry, such as a bend, curve, or contoured shape, without removing any material.
2. Blanking
Blanking is one of the most common stamping operations. The press cuts out a specific shape from the sheet metal. The “blank” can either be the finished part or a piece that moves on to other processes.
3. Drawing
Drawing is used when deeper shapes are needed, such as cups, containers, or housings. It stretches the metal into a new form, using tension to create depth without cracking.
4. Piercing
Piercing is the opposite of blanking. Instead of keeping the cut-out shape, piercing removes material from the sheet to create holes or openings.
5. Progressive Die Stamping
Some parts require multiple operations. Progressive die stamping does this in one continuous process. The metal strip moves through several stations within one press, with each station performing a different operation such as cutting, bending, forming, and trimming until the part is complete.
This approach delivers:
- High speed
- Tight tolerances
- Consistency across large production runs
- Reduced labor and production time
Stamping Press Types
Stamping presses power the dies that shape the metal. The two primary press types include:
Mechanical Presses
- Extremely fast
- Ideal for high-volume production
- Excellent for consistent, repeatable operations
- Often used in progressive die stamping
Hydraulic Presses
- Higher control and precision
- Safer and better for forming thicker metals
- Slower than mechanical presses, but more versatile
Both press types deliver superior accuracy compared to manual machining or traditional cutting and forming tools.
Materials Used in Sheet Metal Stamping
One of the biggest advantages of stamping is its flexibility. Nearly any metal can be stamped if it begins in sheet form.
Common sheet metal stamping materials include:
- Aluminum
- Stainless steel
- Carbon steel (low and high)
- Brass
- Copper
- Bronze
- Nickel alloys
- Titanium
- Inconel
- Beryllium copper
Different metals offer different benefits, such as strength, corrosion resistance, conductivity, or heat tolerance, so the choice depends on the application.
What Industries Use Sheet Metal Stamping?
Because stamping offers precision, repeatability, and cost-effectiveness, it’s used across virtually every major manufacturing sector. Some of the most common applications include:
Automotive
Stamped metal parts support body structures, engine systems, electrical components, and safety features.
Medical
Precision stamping is used to create surgical tools, device housings, and small electronic components.
Industrial & Manufacturing
From brackets to enclosures, stamping is ideal for durable, high-strength parts.
Aerospace
Tight tolerances and lightweight materials make stamping a go-to method for aerospace components.
Renewable Energy
Solar panel frames, wind turbine components, and electrical hardware often rely on stamped parts.
Hardware & Home Improvement
Lighting fixtures, brackets, fasteners, and appliance parts are commonly stamped.
Simply put, if a product includes metal components, sheet metal stamping likely plays a role in its creation.
Benefits of Sheet Metal Stamping
Sheet metal stamping offers several advantages over other manufacturing methods, especially for medium- to high-volume production:
1. High Precision
Dies are engineered to extremely tight tolerances, producing consistent, repeatable parts.
2. Fast Production
Progressive die stamping allows large volumes of parts to be made in minutes.
3. Cost-Efficiency
Reduced labor, faster cycles, and less scrap mean lower overall production costs.
4. Versatility
Stamping supports a wide range of shapes, from simple brackets to complex multi-step components.
5. Short Lead Times
Automated processes speed up prototyping and production, helping manufacturers meet tight deadlines.
6. Ideal for Custom Parts
Custom sheet metal stampings follow the same process as standard parts—they’re simply engineered to the client’s unique specifications.
How Custom Sheet Metal Stampings Differ
While the stamping process is the same, custom parts are designed around:
- Specific thickness
- Unique geometries
- Tighter tolerances
- Special materials
- Low- or high-volume production needs
Whether a customer needs short-run prototyping or full-scale production, custom stampings ensure the part meets exact design requirements.
Key Takeaways
- Sheet metal stamping transforms flat metal sheets into precise, high-quality components.
- Common processes include forming, blanking, drawing, piercing, and progressive die stamping.
- Nearly any metal can be stamped, including aluminum, stainless steel, copper, and nickel alloys.
- Industries from automotive to aerospace rely on stamped components.
- Stamping offers speed, accuracy, cost savings, and versatility for complex part production.
- Custom stampings use the same process but are built to unique design specifications.
Ready for High-Quality Stamped Metal Parts?
Whether you need short-run stampings, large-volume production, or complete metal fabrication services, Fox Valley Stamping delivers precision, quality, and reliability.
Our team provides expert engineering support, fast turnaround times, and comprehensive secondary operations—including assembly, welding, and finishing. Contact Fox Valley Stamping today for a free quote or to learn more about our custom sheet metal stamping capabilities.